Artificial Neural Networks
FEF3001 Yapay zekaya giriş - Hafta7
2024-11-14
Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are systems developed to automatically perform capabilities such as learning through new information, creating new information, and making discoveries - similar to characteristics of the human brain - without any external assistance.
The most basic task of an ANN is to determine an output set corresponding to an input set presented to it. To achieve this, the network is trained with examples of the relevant event (learning) to acquire generalization ability. Through this generalization, output sets corresponding to similar events are determined.
Biological Connection
A biological nerve cell is the fundamental building block that enables the human brain to function. A neural network is formed by billions of nerve cells coming together. An Artificial Neural Cell (ANC) mimics biological nerve cells to achieve learning and uncover relationships between phenomena. Information is transmitted between nerve cells in a manner similar to a real neural network.
Application Areas of ANNs
- Function Approximation
- Time Series Analysis
- Regression
- Classification
Function Approximation
Let x = {x₁, x₂, …, xₙ} be a vector and y = f(x) be a function associated with it. Although the function is unknown, there are x vectors and corresponding y values. Thus, to find the y value according to a given xₙₑw, the function needs to be estimated (approximated). As seen, in an ANN, input neurons will be n in number representing x, while output neurons will be one in number representing y.
Time Series Analysis
Time series future value prediction is a very general problem. There are various statistical approaches for such a problem. When time is represented by t, the function xᵗ = f(xᵗ⁻¹, xᵗ⁻², xᵗ⁻³, …) can be estimated to predict future values. Many business and economic time series analyses show seasonal and trend-based variations.
Regression
Regression is the process of creating a prediction function between independent variables and the dependent variable. For ANN, independent variables are represented by input neurons, while dependent variables are represented by output neurons. While the number of independent variables is insignificant in regression analysis, the dependent variable can only be one. However, in ANNs, since both input and output neurons can be determined as desired, both the number of independent variables and dependent variables become insignificant.
Classification
Classification can be defined as determining which group an object belongs to based on its characteristics. For example, in a bank, it’s possible to divide loan applicants into two classes such as “can be given credit” or “cannot be given credit” based on various characteristics like monthly income, assets, and education level. For this purpose, the ANN’s input neurons will represent the objects’ characteristics, while output neurons will represent the class it belongs to. In this example, there are two classes, and this situation is called binary decision. Assume that either logistic transformation function or hyperbolic tangent transformation function is used in the output neuron.
Classification (cont’d)
In cases where the number of classes increases, multiple cells may need to be used in the output layer. For example, in a situation with four classes, four cells can be used in the output layer, and each cell corresponds to one class. When using the logistic transformation function in each neuron, neurons with values close to 0 represent not belonging to the relevant class, while those close to 1 represent belonging to the relevant class.
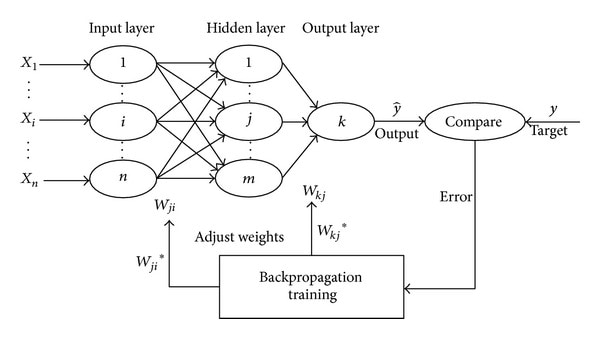
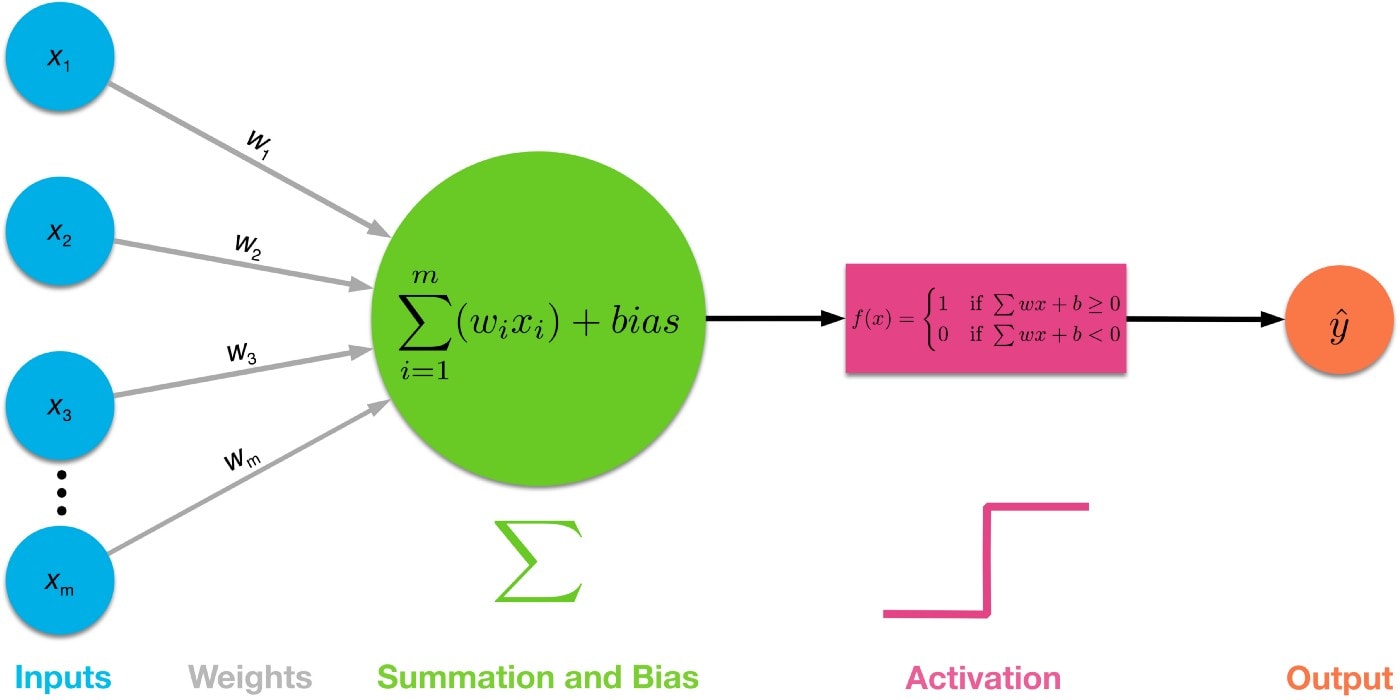
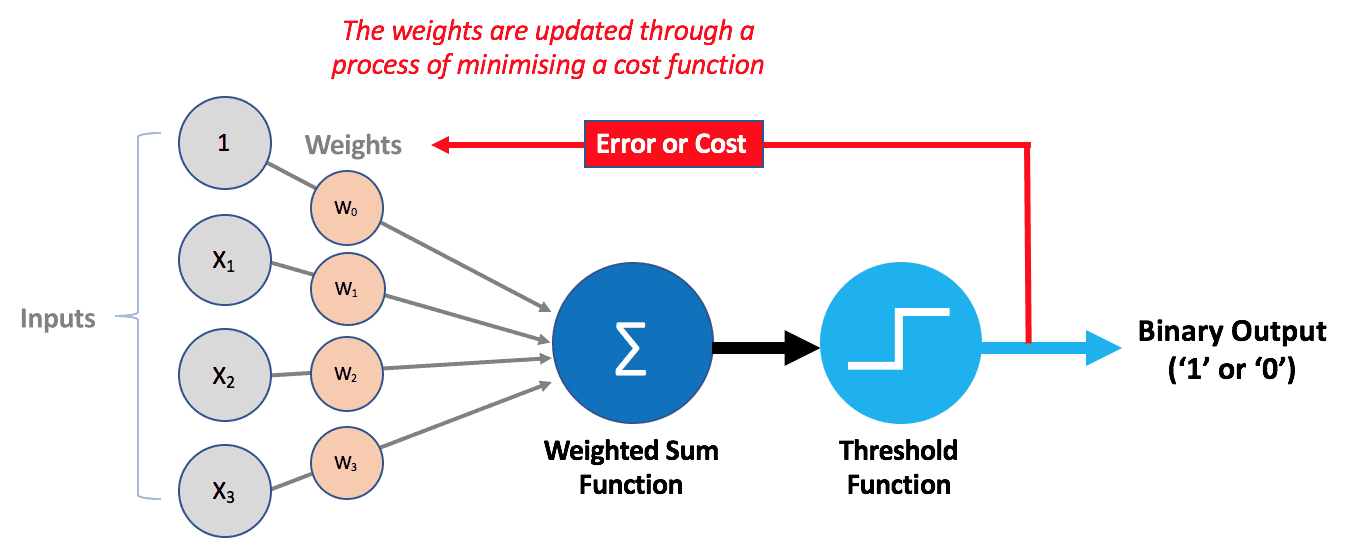
Neural Cell Structure
An ANN consists of five parts
- Inputs (x₁, x₂, …, xₙ)
- Weights (w₁, w₂, …, wₙ)
- Combination (summation) function
- Activation function
- Output
ANN neuron cell
Common Combination Functions
| Function | Equation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Addition | NET = Σᵢ₌₁ⁿ xᵢwᵢ | NET value is obtained by summing the products of input and weight values |
| Multiplication | NET = ∏ᵢ₌₁ⁿ xᵢwᵢ | NET value is obtained by multiplying the products of input and weight values |
| Maximum | NET = Max(xᵢwᵢ) | NET value is obtained from the largest of the products of input and weight values |
| Minimum | NET = Min(xᵢwᵢ) | NET value is obtained from the smallest of the products of input and weight values |
| Sign | NET = Sgn(xᵢwᵢ) | The number of positive and negative values from the products of input and weight values is found, and the larger value is accepted as the NET value |
Common Activation Functions
Identity Function
- A commonly used linear function
- g(x) = x
Common Activation Functions
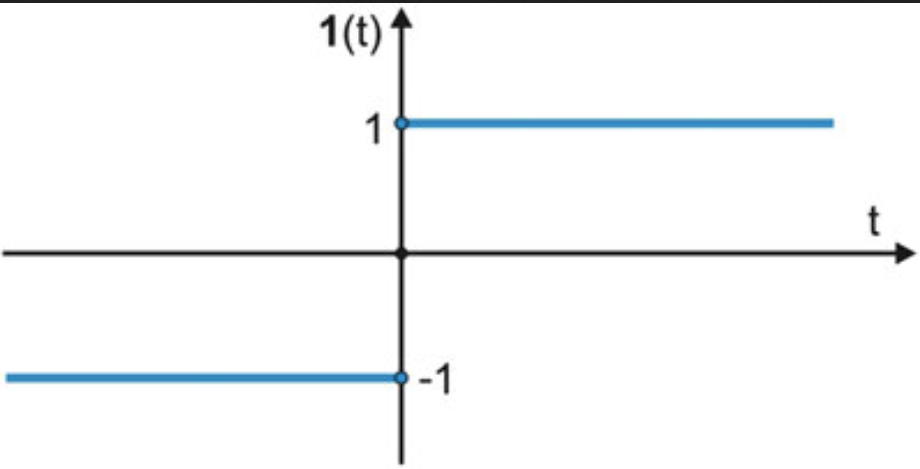
Step Function
- Generally used in single-layer networks
- g(x) = {
- b if x ≥ c
- a if x < c }
- b if x ≥ c
- Where c = 0, a = 0, b = 1 or
- c = 0, a = -1, b = 1 are preferred
Step function for c=0, b=1 and a=-1
Common Activation Functions
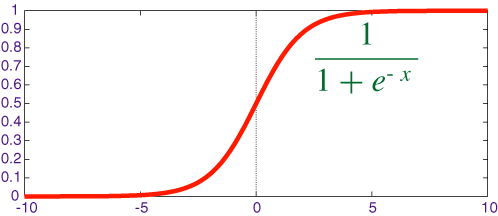
Sigmoid (Logistic) Function
- Keeps the value nᵢ in a cell within [0,1] range
- The t parameter is used as a type of sensitivity level
- Particularly advantageous in networks trained with backpropagation
- Sigmoid function output is in [0,1] range
- g(x) = 1/(1 + e⁻ˣ/ᵗ)
Common Activation Functions
Hyperbolic Tangent Function
- Similar to logistic activation function
- Keeps the value nᵢ in a cell within [-1,1] range
- g(x) = (eˣ/ᵗ - e⁻ˣ/ᵗ)/(eˣ/ᵗ + e⁻ˣ/ᵗ)
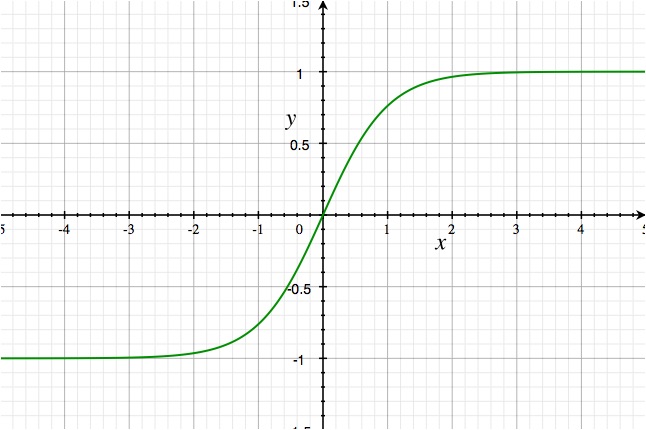
Summary of activation functions
see the next slide
Perceptron
ANN